About us
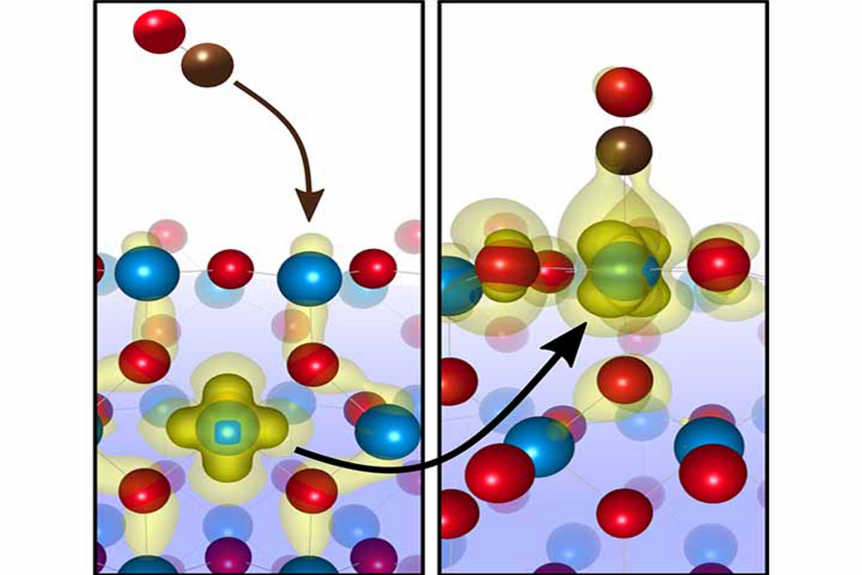
Computational materials science is one of the fastest developing fields in Physics and Chemistry. It is focused on the investigation of the complex properties of solids and liquids on an atomistic scale - making a quantum-mechanical description of the interaction between atoms and electrons mandatory.
Although the basic concepts of quantum mechanics have been discovered about 80 years ago, a wide-scale application on materials science has only become feasible in the last decades. Based on the development of density functional theory (DFT) by Walter Kohn, systems of several hundred atoms can be routinely simulated on present-day computers.
The Vienna ab-initio Simulations Package (VASP), which has been developed in our group, is one of the most efficient implementations. At the moment, VASP is used by more than 1000 research groups in industry and academia worldwide. It is also used as a common tool within most of the research projects in our group.
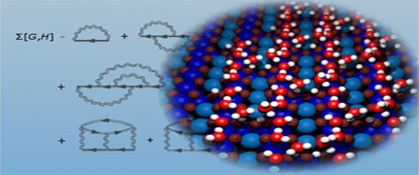
In the further development of the VASP features, we concentrate on modern methods from quantum field theory and quantum chemistry.
However, the basis for most applications is and remains Walter Kohn's density functional theory. This groundbreaking method allows us to calculate systems with up to several thousand atoms on powerful parallel computers.